The influence of polarization voltage on the electrical properties of the magnetic fluid layer filling the inter electrode space of a planar parallel capacitor connected to a series resonant circuit. The formation, development, and self-organization of aggregates several millimeters in size have been recorded in the magnetic fluid layer, which affects its electrical and physical properties.
The changes in the electrical and physical properties of magnetic fluids in the presence of structural formation in an electric field have been studied in many works. Structure formation under the influence of weak electric fields up to 400 kV/m. The average size of the formed structures was found to be no more than a few micrometers, and their appearance is related to the increase in dispersed phase concentration near the electrode and subsequent aggregation. The aggregation process was explained based on the thermodynamic concept of phase transition. As is well known, due to the strong influence of external environments on various environments, qualitative new structural forms related to self-organization phenomena may emerge.
The circuit of the experimental setup is a series resonant circuit. It consists of a standard inductor coil L=0.22 H and a capacitor made of two parallel glass plates with a conductive coating on one side and a layer of magnetic fluid between them. The thickness of the magnetic fluid layer is determined by the dielectric gasket; The unit design enables the provision of a constant electric field Ep with a strength of up to 5000 kV/m. We used a kerosene based magnetic fluid and stabilized magnetite particles with oleic acid, with a solid phase volume concentration of 2%.
A sine voltage with an effective value U=1.5 V and variable frequency is provided by the generator to the input of the series resonant circuit. Resonance is achieved by changing the frequency of the input voltage and is determined by the maximum value of the alternating current passing through the circuit. The current in the circuit is calculated from the voltage drop Rs=100 W across the shunt, which is measured using a voltmeter. Apply polarization voltage to the battery from a constant voltage source and record it with a voltmeter.
In transmitted light, visually record a size of 0.1 The shape and size of a 5mm structure depend on the magnitude of the polarization voltage and its exposure time. Therefore, as the polarization electric field strength increases, the structure formation increases, and first from the cell to the maze, and then to the fractal cluster. Simultaneous observation in the reflected light of interference patterns on the cell surface indicates the presence of an automatic wave process.
As shown in the figure. As shown in the figure, the variation of resonant current depends on the polarization voltage of each layer thickness, which is attributed to the change in battery conductivity. On the contrary, due to the appearance of aggregates, their structure and self-organization, as well as changes in conductivity, will also occur. The smaller the thickness of the magnetic fluid layer, the greater the change in resonant current under the influence of the electric field. Under the polarization voltage of 20-30 V, the observed layer thickness is 20 The structure of 40 μ t has the form of a vortex, with spiral waves diverging from the center.
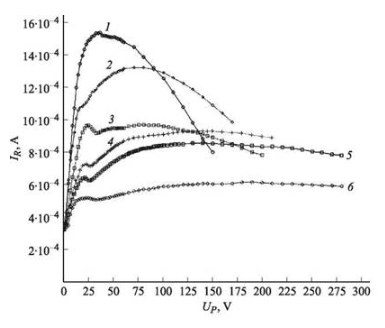
Within the polarization voltage range of 20-30 V, the magnetic fluid layer is 80 The existence of a maximum resonant current of 220 mm is related to the synchronization of the automatic wave process. Increasing the layer thickness from 80 to 220 mm will not affect the characters.
The dependence of resonant current on polarization voltage. The results were observed to have good reproducibility, with a random error not exceeding 1.5%.
It has been found that the magnitude of the resonant current in the circuit and therefore the conductivity of the battery in the absence of polarization voltage do not depend on the thickness of the magnetic fluid layer. Therefore, under these conditions, the electrical performance is determined by the near electrode region with low conductivity. The effect of polarization voltage on batteries with magnetic fluids can lead to the coordinated movement of charge carriers, manifested as the formation of observed structures. As the thickness of the magnetic fluid layer decreases, the property change of the dependence of the resonant current of the circuit on the polarization voltage is related to the reduction of the number of magnetite particles in the inter electrode space involved in the formation of dissipative structures.




















